Energy drinks have become a staple for those looking for an extra boost throughout the day, whether you’re powering through work, exercise, or a late-night study session. Among the most popular brands is NOS Energy Drink, known for its bold flavor and high-energy formula.
But if you’re a health-conscious consumer or curious coffee drinker wondering: “Does NOS Energy Drink have caffeine?”—you’re not alone.
NOS Energy Drink does contain a significant amount of caffeine – 160mg per 16 fl oz can. This puts it on par with other leading energy drinks and roughly equivalent to two cups of coffee.
Understanding its complete ingredient profile, nutritional impact, and potential side effects is crucial before deciding to make it part of your daily routine.
Whether you’re a coffee aficionado comparing caffeine sources, a health-conscious consumer evaluating your beverage choices, or someone experiencing concerning side effects.
This comprehensive guide will provide you with the evidence-based information you need to make informed decisions about NOS Energy Drink consumption.
Does NOS Energy Drink Contain Caffeine?
Yes, NOS Energy Drink contains caffeine as one of its key active ingredients that provides stimulating effects. Understanding the precise caffeine concentration helps you manage your daily intake and compare different beverages effectively.
NOS Energy Drink Caffeine Content Per 100ml
Per 100ml: 33.81mg caffeine Per 16 fl oz can (473ml): 160mg caffeine Per 8 fl oz serving: 80mg caffeine
This means that a standard 473ml can of NOS delivers 160 milligrams of caffeine, placing it in the moderate-to-high range of caffeinated beverages.
How NOS Compares to Other Beverages
To put NOS in perspective for coffee enthusiasts and caffeine consumers:
- NOS Energy Drink: 33.81mg per 100ml
- Red Bull: 32mg per 100ml
- Monster Energy: 33mg per 100ml
- Bang Energy: 113mg per 100ml
- Brewed Coffee: 40-95mg per 100ml
- Espresso: 212mg per 100ml (consumed in smaller quantities)
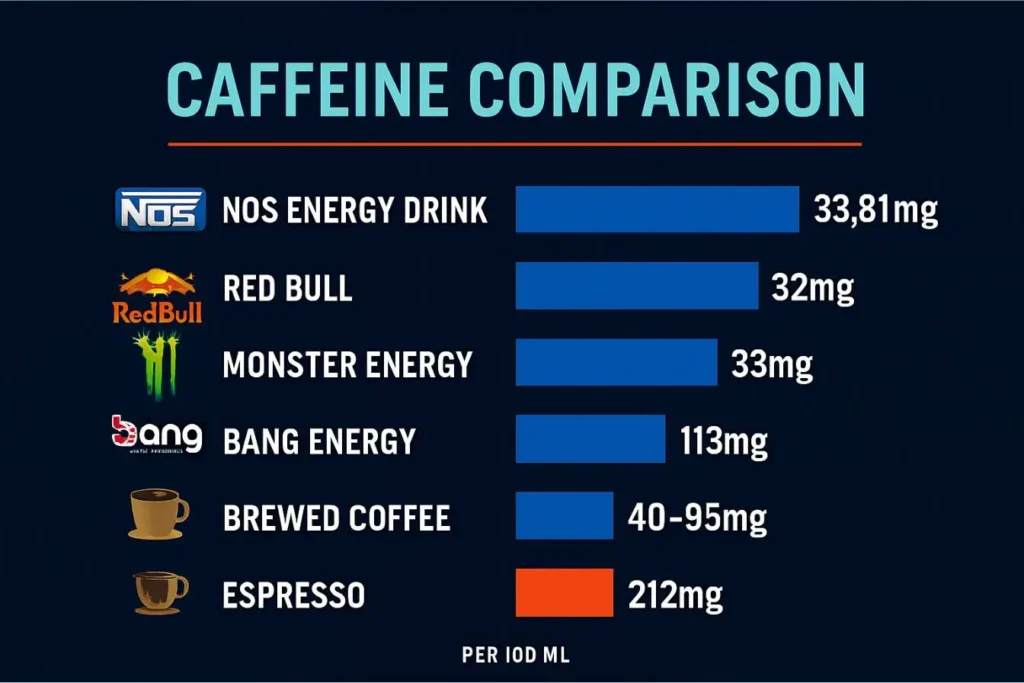
NOS contains similar caffeine levels to other mainstream energy drinks like Red Bull and Monster, making it a comparable choice in terms of stimulant content.
Caffeine Absorption and Effects
The caffeine in NOS is synthetic caffeine, which is absorbed more rapidly than naturally occurring caffeine found in coffee. This means you may feel the effects within 15-30 minutes, but the duration might be shorter compared to coffee consumption.
The general guideline is that 400 milligrams of caffeine per day is safe for most healthy adults, so a single can of NOS represents 40% of this recommended daily limit.
Caffeine in NOS Energy Drinks
- Caffeine Content: A standard 16 oz can of NOS Energy Drink contains approximately 160mg of caffeine.
- Additional Ingredients: NOS features a “CMPLX6” blend with ingredients like Taurine and Guarana.
- Other Features: NOS Original flavor is described as a tropical citrus with mango and passionfruit notes.
- Daily Limit: For healthy adults, the FDA recommends a daily caffeine limit of 400mg.
NOS Energy Drink Ingredients
The ingredients in NOS Energy Drink are designed to provide a quick energy boost while enhancing endurance and focus. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the components that make up this popular beverage:
Primary Active Ingredients
Caffeine (160mg per can): The primary stimulant responsible for increased alertness, mental focus, and physical energy.
Taurine (1000mg per can): An amino acid that helps regulate various bodily functions. Taurine is often included in energy drinks for its potential to improve exercise performance and mental focus, though scientific evidence on its benefits remains mixed.
Glucuronolactone (600mg per can): A naturally occurring compound believed to support energy production and reduce fatigue, commonly found in energy drink formulations.
B-Vitamins Complex: NOS contains essential B-vitamins including:
- B3 (Niacin): Supports energy metabolism
- B6 (Pyridoxine): Helps convert food into energy
- B12: Crucial for energy production and nervous system function
Complete Ingredient Profile
Sweetening Agents:
- Regular version: Contains sugar for quick energy
- Sugar-free version: Uses artificial sweeteners like aspartame and acesulfame potassium
Additional Components:
- Carbonated water
- Natural and artificial flavors
- Citric acid
- Sodium benzoate (preservative)
- Potassium sorbate (preservative)
- Various artificial colors
Ingredient Considerations
For Health-Conscious Consumers: The regular version contains significant sugar content, while the sugar-free version relies on artificial sweeteners.
For Coffee Purists: Unlike coffee’s simple, natural ingredient profile, NOS contains multiple synthetic additives and preservatives.
For Sensitive Individuals: The combination of artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives may trigger reactions in some people.
Is NOS Energy Drink Bad for You?
The safety of NOS Energy Drink depends on several factors, including your health status, caffeine tolerance, and consumption frequency. Let’s examine both the potential benefits and risks.
Potential Benefits
Enhanced Mental Performance: The 160mg caffeine content can improve focus, alertness, and cognitive performance for 3-6 hours.
Exercise Performance: Some studies suggest taurine and caffeine combinations may enhance physical performance, particularly during endurance activities.
Convenience: Provides a quick, portable energy boost without preparation time.
Vitamin Support: B-vitamins contribute to energy metabolism and nervous system function.
Health Concerns and Risk Factors
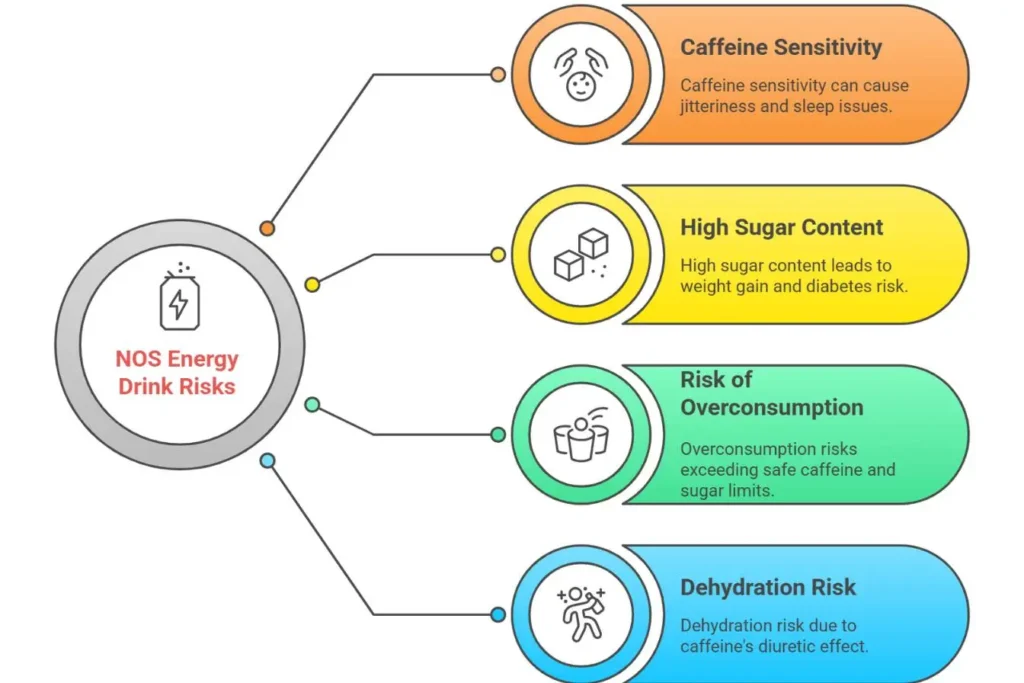
1. Caffeine Sensitivity
If you’re sensitive to caffeine, NOS Energy Drink may cause unwanted side effects such as jitteriness, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, or trouble sleeping. People with lower caffeine tolerance should monitor their intake carefully.
2. High Sugar Content (Regular Version)
A 473ml can contains approximately 54 grams of sugar – that’s about 13.5 teaspoons. This excessive sugar intake can contribute to:
- Weight gain and obesity
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes
- Tooth decay and dental problems
- Blood sugar spikes and crashes
3. Risk of Overconsumption
Energy drinks are often consumed quickly, leading to unknowing excessive intake of caffeine and sugar. Since NOS contains 160mg of caffeine, consuming multiple cans could easily exceed safe daily limits.
4. Dehydration Risk
Energy drinks are not effective for hydration. The caffeine in NOS acts as a mild diuretic, potentially contributing to dehydration, especially during physical activity.
Who Should Avoid NOS Energy Drink?
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Children and adolescents under 18
- Individuals with heart conditions or high blood pressure
- People with anxiety disorders or panic attacks
- Those taking medications that interact with caffeine
- Individuals with diabetes (regular version due to high sugar content)
NOS Energy Drink Nutrition Facts
Understanding the complete nutritional profile helps you make informed decisions about incorporating NOS into your dietary routine.

Regular NOS Energy Drink (473ml can)
- Calories: 220
- Total Fat: 0g
- Sodium: 200mg (8% daily value)
- Total Carbohydrates: 55g (18% daily value)
- Sugars: 54g
- Protein: 0g
- Caffeine: 160mg
Key Active Compounds per Can
Taurine: 1000mg
Glucuronolactone: 600mg
B-Vitamins: Various amounts including Niacin, B6, and B12
Sugar-Free Version
- Calories: Typically 10-25 calories
- Sugars: 0g
- Artificial Sweeteners: Aspartame, acesulfame potassium
- Other nutrients: Similar to regular version
Nutritional Impact Analysis
Sugar Concern: The 54g of sugar in regular NOS represents more than the American Heart Association’s recommended daily limit for added sugars (25g for women, 36g for men).
Caloric Density: At 220 calories per can, NOS provides energy primarily from simple sugars rather than complex nutrients.
Micronutrient Profile: While NOS contains B-vitamins, it provides minimal other essential nutrients compared to whole food sources.
NOS Energy Drink Side Effects
Like most energy drinks, NOS can cause several side effects, particularly when consumed in excess or by sensitive individuals.
Immediate Side Effects (Within 1-6 Hours)
Cardiovascular Effects:
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia)
- Elevated blood pressure
- Heart palpitations
- Chest tightness in sensitive individuals
Neurological Effects:
- Jitters and nervousness
- Anxiety or panic attacks
- Restlessness and agitation
- Difficulty concentrating (paradoxically in some people)
Physical Symptoms:
- Headaches
- Nausea or upset stomach
- Digestive discomfort
- Increased urination
Sleep-Related Side Effects
Sleep Disruption: Consuming NOS too close to bedtime may lead to:
- Difficulty falling asleep (insomnia)
- Reduced sleep quality
- Early morning awakening
- Next-day fatigue and grogginess
Timing Recommendations: Avoid consuming NOS within 6-8 hours of planned bedtime to minimize sleep interference.
Long-Term Health Considerations
Caffeine Dependence:
Regular consumption can lead to physical dependence, with withdrawal symptoms including:
- Severe headaches
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Irritability and mood changes
- Difficulty concentrating
- Flu-like symptoms
Metabolic Effects:
Frequent consumption of high-sugar versions may contribute to:
- Weight gain
- Insulin resistance
- Increased risk of metabolic syndrome
Dental Health Impact:
The combination of sugar and acids can cause:
- Tooth enamel erosion
- Increased cavity formation
- Gum irritation and inflammation
Managing and Minimizing Side Effects
- Gradual Reduction: If experiencing dependence, reduce consumption gradually rather than stopping abruptly.
- Hydration: Increase water intake to counteract caffeine’s diuretic effects.
- Timing Strategy: Consume NOS early in the day to avoid sleep disruption.
- Monitor Total Intake: Consider all caffeine sources throughout your day, including coffee, tea, and chocolate.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact a healthcare provider immediately if you experience:
- Severe chest pain or irregular heartbeat
- Persistent severe headaches
- Signs of allergic reaction (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
- Severe nausea or vomiting
- Panic attacks or severe anxiety
Conclusion
NOS Energy Drink contains 160mg of caffeine per 16 fl oz can (33.81mg per 100ml), placing it among mainstream energy drinks in terms of stimulant content. While it can provide effective energy enhancement and improved focus through its combination of caffeine, taurine, and B-vitamins, the regular version also contains 54 grams of sugar, which raises significant health concerns.
The key to safely incorporating NOS into your routine lies in understanding your individual caffeine tolerance, choosing appropriate timing, and practicing moderation. For health-conscious consumers, the sugar-free version may be preferable, though it still carries the risks associated with high caffeine intake and artificial additives.
For coffee enthusiasts seeking cleaner energy sources, consider that while NOS provides convenience and additional compounds like taurine, traditional coffee offers similar caffeine benefits with fewer additives and more antioxidants.
Natural alternatives like green tea, matcha, or cold brew coffee may provide sustained energy with additional health benefits.
Remember that sustainable energy comes from adequate sleep, proper nutrition, regular exercise, and proper hydration. Energy drinks should supplement, not replace, these fundamental health practices.
Ready to make an informed decision about your energy drink consumption?
Start by tracking your total daily caffeine intake from all sources for one week, noting how different beverages affect your energy levels, sleep quality, and overall well-being. This personal assessment will help you determine whether NOS Energy Drink fits appropriately into your lifestyle and health goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How much NOS Energy Drink is safe to consume per day?
Most health experts recommend limiting energy drink consumption to one can per day maximum. Since NOS contains 160mg of caffeine per can and the FDA recommends no more than 400mg of caffeine daily for healthy adults, you could theoretically consume 2.5 cans. However, considering the high sugar content (54g per can) and other stimulants, one can per day is the safer limit. Pregnant women, teens, and those with heart conditions should avoid energy drinks entirely.
2. When is the best time to drink NOS Energy Drink?
The optimal time to consume NOS Energy Drink is during the morning or early afternoon, ideally before 2 PM. This timing allows the caffeine to provide energy when you need it most while ensuring it doesn’t interfere with your sleep cycle. Avoid drinking NOS within 6-8 hours of bedtime, as the 160mg of caffeine can significantly disrupt sleep quality and duration.
3. Can I mix NOS Energy Drink with alcohol?
No, mixing NOS Energy Drink with alcohol is extremely dangerous and strongly discouraged. The combination can mask alcohol’s depressant effects, leading to overconsumption and increased risk of alcohol poisoning. The stimulants in NOS can also put additional stress on your cardiovascular system when combined with alcohol, potentially causing dangerous heart rhythm irregularities.
4. Is NOS Energy Drink worse than coffee?
From a caffeine standpoint, NOS (160mg per can) and coffee (95-200mg per cup) are comparable. However, NOS contains 54g of added sugar, artificial ingredients, and preservatives that coffee lacks. Coffee provides antioxidants and has been linked to various health benefits, while energy drinks like NOS primarily offer stimulation with potential negative effects from high sugar content. For health-conscious consumers, black coffee or coffee with minimal natural sweeteners is generally the better choice.
5. What should I do if I experience side effects from NOS Energy Drink?
If you experience mild side effects like jitters, headache, or stomach upset, stop consuming NOS immediately and drink plenty of water. These symptoms typically resolve within 4-6 hours as caffeine levels decrease. For severe symptoms like chest pain, irregular heartbeat, severe anxiety, or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately. To prevent future issues, consider reducing your caffeine intake, choosing smaller serving sizes, or switching to lower-caffeine alternatives like green tea.

